Abstract
Background
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has emerged as a promising therapeutic option for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. However, access to CAR T cell therapy remains limited as CAR T cells are routinely administered in the hospital setting. Hence, there's a growing interest in standardizing outpatient administration of CAR T cells to increase patient access and minimize costs. Here, we describe our institution's experience with outpatient administration of CAR T cells.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we reviewed who received CAR T cell therapy in the outpatient setting at Karmanos Cancer Center between June 2019 and June 2021.Charts were reviewed for age, disease pathology, prior lines of therapy, need for hospitalization within 30 days, development of CRS and/or neurotoxicity, need for ICU admission, need for steroids and/or tocilizumab, length of admission, and disease state at last follow up. All patients received fludarabine and cyclophosphamide as lymphodepletion (LD) therapy day -5 to -3. CAR T cells were infused on day 0. Patients subsequently followed up in clinic daily for 2 weeks and were started on allopurinol, ciprofloxacin, fluconazole, acyclovir and levetiracetam. First response was assessed by FDG PET scan 4 weeks after CAR T cell .
Results
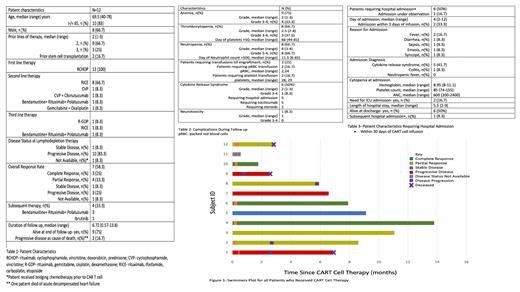
A total of 12 patients received CAR T cells during the study period. All patients had a diagnosis of DLBCL and received Tisagenlecleucel. Median age at CAR T cell therapy was 69.5 years (40-78 years). Median number of prior lines of therapy was (2-3) while 2 patients had received prior stem cell transplantation. Table 1 describes patient characteristics and lines of therapy. Two patients received bridging therapy prior to LD. Overall response rate was 58.3% (complete response-3, partial response-4). Median duration of follow up was 6.7 (0.6-13.8 months). Four patients required subsequent therapy after CAR T cell for disease progression while 9 patients were alive at the time of data cut off. Figure 1 summarizes disease response and follow .
Table 2 summarizes complications during follow up. Nine (75%) patients developed anemia (grade 3-4 n=4, 33.3%), 8 (66.7%) developed thrombocytopenia (grade 3-4 n= 3, 37.5%), and 8 (66.7%) developed neutropenia (grade 3-4 n=8, 66.7%). Median time to platelet recovery to >,000 and neutrophil recovery to >500 was 66 days (44-81 days) and 11.5 days (6-65 days), respectively. Three (25%) patients required platelet and red blood cell transfusion support. Six (50%) patients developed cytokine release syndrome (CRS) with median grade 2 (range 1-3, grade 3-4 n=1). Five (5/6) patients required hospitalization, five (5/6) required tocilizumab, and one (1/6) required steroids. One (8.3%) patient developed neurotoxicity of grade 1 severity improved without systemic therapy.
Six patients required hospitalization within 30 days of CAR T cell infusion. Median day of admission from CAR T cell infusion was 4 days (range 2-12 days (range 2-12 days, admission within 3 days n=2, admission under observation n=1). Patient characteristics at admission are summarized in table 3. Of these, 5 patients were diagnosed with CRS,1 patient with colitis and none with blood stream infection. Two patients required ICU admission. Median length of hospital admission was 5.5 days (2-9 days). All patients were alive at discharge while 1 patient required subsequent admission within 30 .
Conclusion
Outpatient administration of Tisagenlecleucel is feasible with low risk of hospital admission within 3 days of infusion. Adoption of outpatient CAR T cell therapy may increase patient access for treatment of DLBCL and diseases such as multiple myeloma while reducing administration costs for this novel therapy.
Modi: Genentech: Research Funding; Seagen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MorphoSys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Deol: Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal